With the Internet of Things development, radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is increasingly being applied to industrial sites. The full English name of RFID is “Radio Frequency IdentificatIon”. It is a wireless identification technology that was born in the 1950s, which can use radio to perform identification without contact.
According to different radio frequencies, RFID systems can be divided into four types: low frequency, high frequency, ultra-high frequency, and microwave.
Low-frequency system (LF): RFID radio wave frequency is lower than 134KHz system, following the ISO/IEC 18000-2 standard;
High-frequency system (HF): RFID radio wave frequency at 13.56MHz system, by ISO/IEC 15693 (compatible with ISO/IEC 18000-3), ISO14443 standards.
Ultra-high frequency system (UHF): RFID radio wave frequency between 860~960MHz system, following the ISO/IEC 18000-6B/C standard;
Microwave system (Microwave): RFID radio wave frequency in 2.4GHz system, following the ISO/IEC 18000-4 standard;
An RFID system generally consists of four parts: electronic tags, antennas, readers, and application software.
Electronic tags can be divided into low-frequency electronic tags, high-frequency electronic tags, ultra-high frequency electronic tags, and microwave electronic tags according to different frequencies; The electronic label is similar to the barcode in the barcode system, which integrates a chip that can be erased and written to store information. According to whether it is equipped with a battery, electronic tags are divided into two types: active and passive. The active electronic tag has a battery, and the readable distance is longer compared with the passive electronic tag.
Low-frequency radio frequency tags
Low-frequency radio frequency tags, referred to as low-frequency tags for short, have an operating frequency range of 30kHz ~ 300kHz. Typical operating frequencies are 125KHz and 133KHz.
Low-frequency tags are generally passive tags, and their working energy is obtained from the radiated near field of the coupling coil of the reader through inductive coupling. When transmitting data between a low-frequency tag and a reader, the low-frequency tag needs to be located in the near-field area radiated by the reader antenna. The reading distance of low-frequency tags is generally less than 1 meter.
Typical applications of low-frequency tags are animal identification, container identification, tool identification, electronic lock theft prevention (car keys with built-in transponders), etc. International standards related to low-frequency tags are ISO11784/11785 (for animal identification), and ISO18000-2 (125-135 kHz). How many low-frequency tags are there?
There are various appearance forms, and the appearance of low-frequency labels used in animal identification include collar type, ear tag type, injection type, pill type, etc. Typical applications of animals are cattle, pigeons, and so on.
The main advantages of low-frequency tags are: tag chips generally use ordinary CMOS technology, which is power-saving and cheap; the operating frequency is not restricted by radiofrequency regulation; it can penetrate water, organic tissue, wood, etc.; it is very suitable for close-range, low-speed, data-required recognition applications (eg: animal recognition), etc.
The disadvantages of low-frequency tags are mainly reflected in: tags store fewer data; they can only be used for low-speed, close-range identification applications; compared with high-frequency tags: tag antennas have more turns and higher costs.
High-frequency radio frequency tags
The operating frequency of high-frequency radio frequency tags is generally 3MHz ~ 30MHz. The typical working frequency is: 13.56MHz, and its working energy is the same as that of the low-frequency tag, and it is also obtained from the radiated near field of the coupling coil of the reader through inductive (magnetic) coupling.
Because high-frequency tags can be easily made into a card shape, typical applications include electronic tickets, electronic ID cards, electronic locking and anti-theft (electronic remote control door lock controllers), etc. Relevant international standards are ISO14443, ISO15693, ISO18000-3 (13.56MHz), and so on.
UHF tags (frequency between 860MHz and 960MHz)
High-frequency systems transmit energy through electric fields. The energy of the electric field does not drop very fast, but the reading area is not well defined. The reading distance of this frequency band is relatively far, and the passive can reach about 10m. It is mainly realized through capacitive coupling.
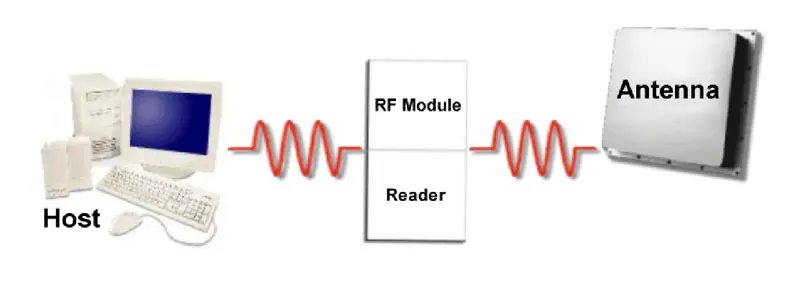
Antenna: generally connected to the reader to receive/send electromagnetic waves;
Reader: used to read the data of the electronic tag and transmit it to the upper computer application software system; some can also write data to the electronic tag;
Application software: PC or PLC-based software system used to process the data sent by the reader.
The RFID system is shown in the figure below:
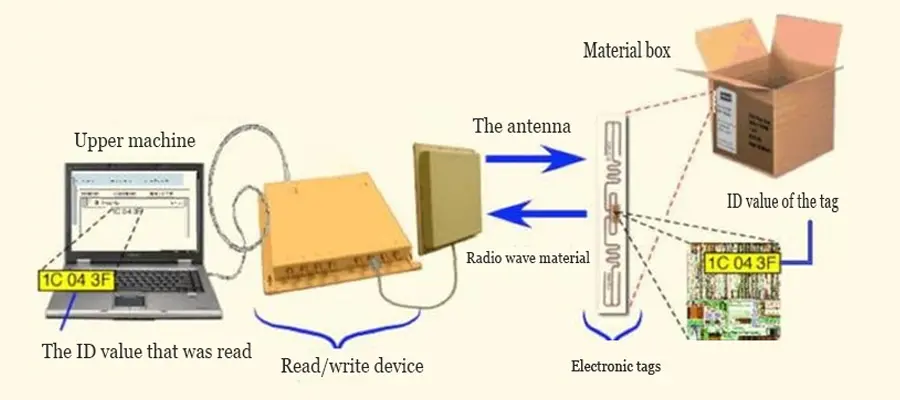
The working principle of the RFID system is as follows: the reader sends electromagnetic waves of a certain frequency through its antenna; when the electronic tag enters the working range of the transmitting antenna, the internal induced current is generated and activated, so the stored information is passed through the internal The antenna is sent out; the reader`s antenna receives the carrier signal from the electronic tag and transmits it to the reader; the reader demodulates and decodes the received signal, and sends the processed data to the upper position Machine or PLC processing system.




